Disk Sanitization Best Practices
Disk Sanitization Best Practices
Data volume and the number of data storage devices have grown exponentially. This has led to the significant increase in the time required for disk sanitization, both in terms of the number of devices and data storage capacities.
A common question that IT managers ask today is: What are the best sanitization methods for each device and what are the criteria for choosing them? This article offers practical guidance for those questions.
DoD 5220.22-M (National Industrial Security Program Operating Manual) was published in 1995, which established the standard procedures and requirements for all government contractors with regards to classified information. This manual specified 3-pass overwrite for HDD sanitization and this 3-pass overwrite is often cited as DoD 5220.22-M compliant method. As it is an old standard, it does not cover new technologies such as SSD, mobile devices, etc.
Sanitization methods are now deferred to Defence Security Service, a U.S. Department of Defence (DoD) agency, and DSS manual specifies NIST 800-88 for disk sanitization.
Types of Sanitization
The NIST 800-88 Rev1 publication describes three types of media sanitization: clear, purge, and destroy, which can help ensure that data is not unintentionally released. These types are defined as follows:
- Clear: Applies logical techniques to sanitize data in all user-addressable storage locations for protection against simple noninvasive data recovery techniques; it is typically applied through the standard read and write commands to the storage device, such as by rewriting with a new value or using a menu option to reset the device to the factory state (where rewriting is not supported).
- Purge: Applies physical or logical techniques that render target data recovery infeasible using state-of-the-art laboratory techniques.
- Destroy: Renders target data recovery (using state-of-the-art laboratory techniques) infeasible and results in the subsequent inability to use the media for storage of data.
Following figure is a guide to select best sanitization method out of these 3 types of sanitization. In short, you need to consider:
- Security level of the data stored on the device
- Whether the device will remain under or leave the organizational control
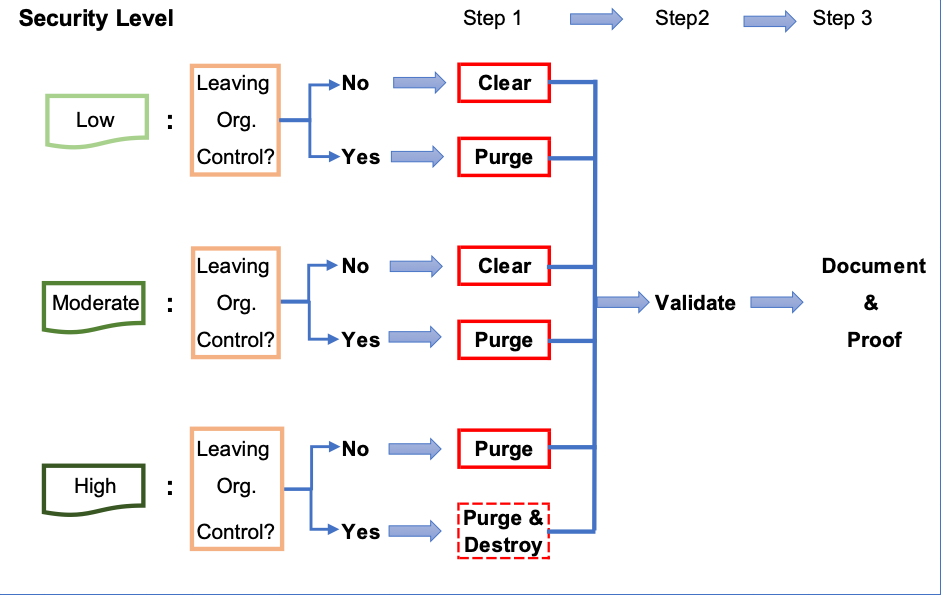
Destruction of a device has become increasingly undesirable for both environmental and cost considerations, because reliable destruction of a device requires specialized machine such as Degaussers. If destruction is being outsourced, you will need to purge data before a device leaves the organization.
16 methods of data sanitization DiskDeleter offers satisfy all the requirements from speedy complete data erasure to high security data purge, and complete the sanitization process all the way through the documentation and proof steps.
For selection of a right deletion method, please see 16 Wipe Methods
© 2024 Jungle KK - Powered By Knowledge Fortune
